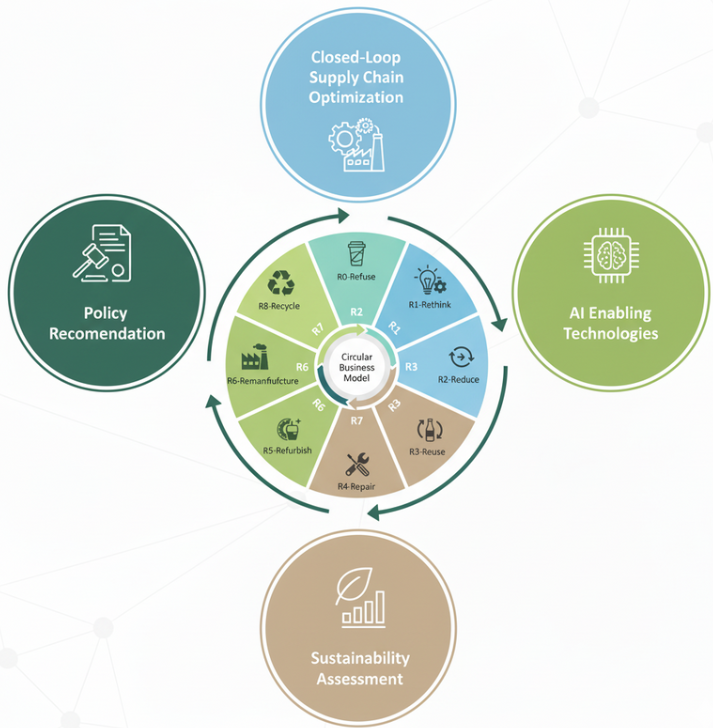
Circular economy isn’t only about recycling. It’s about redesigning how value is created—so materials, components, and products stay productive for longer, and “waste” becomes an asset. At Greenovation Solutions, we help organisations turn regulatory pressure and resource constraints into market opportunities by building circular business models that are practical to implement, financially credible, and scalable across sites and partners.
If you’re exploring battery reuse, product lifecycle extension, industrial symbiosis, or circular supply chains, this service is built to move you from ideas → to an implementation blueprint with techno-economic validation, risk profiling, and go-to-scale pathways.
Why circular business model innovation matters now
Across manufacturing, energy, mobility, and infrastructure, the same pain points keep coming up:
Rising material costs and supply volatility
Tougher environmental rules and reporting requirements
Customer expectations shifting toward low-carbon, repairable, and traceable products
Investor pressure to prove resilience and measurable impact
A circular business model tackles these issues at the system level: it redesigns the value chain so you can reduce dependency on virgin materials, extract more value from assets, and unlock new revenue streams from recovery, remanufacturing, refurbishment, and service-based offerings.
The result is not just “being greener.” It’s a stronger competitive position: lower operational costs, new profit pools, improved compliance, and a brand story backed by real engineering and numbers.
What “Circular Business Model Innovation” means in practice
A business model becomes circular when it is designed to retain value in products and materials through strategies such as:
Product life extension (repair, upgrade, refurbishment, remanufacturing)
Reuse and second-life programs (e.g., EV batteries repurposed for stationary storage)
Waste-to-value (recovering materials or by-products as inputs to another process)
Industrial symbiosis (cross-industry partnerships where one site’s output becomes another’s feedstock)
Circular supply chain integration (reverse logistics, take-back, traceability, quality grading)
The real challenge is not picking a concept. The challenge is designing a model that survives reality: unit economics, quality variability, regulation, liability, partner incentives, and scale-up constraints.
That’s where we focus.
Our approach: from strategy to implementation blueprint
We don’t deliver circularity as a slide deck. We deliver it as an implementation-ready blueprint with validated economics and a clear scale pathway.
1) Diagnose circular value and constraints
We begin by mapping:
Material/product flows (what moves, where value is lost, where waste is created)
Regulatory obligations and compliance risks
Current cost structure and operational bottlenecks
Stakeholders and partner incentives (suppliers, customers, recyclers, logistics)
Outcome: a shortlist of the highest-impact circular opportunities, ranked by feasibility and value.
2) Design circular business model options
We develop alternative models, such as:
Service-based models (Product-as-a-Service, leasing, performance contracts)
Take-back programs with quality grading and resale channels
Refurbishment or remanufacturing loops
Second-life value chains for components (notably batteries and electronics)
Industrial symbiosis networks between nearby sites or across sectors
Outcome: 2–4 business model candidates with clear value propositions and operating assumptions.
3) Techno-economic validation (TEA)
This is where circular ideas become decision-ready. We quantify:
CAPEX/OPEX and operating costs across the new loop
Yield, throughput, and quality grades (including variability)
Pricing scenarios, margin sensitivity, and break-even points
Logistics costs and reverse supply requirements
Market demand assumptions and route-to-market options
Outcome: a TEA model and decision narrative that leadership can approve.
4) Risk profiling and compliance readiness
Circular models often fail due to underestimated risks:
Safety, performance, warranty, and liability
Quality uncertainty in recovered materials/components
Traceability, documentation, and chain-of-custody needs
Regulatory constraints on transport, storage, and processing
We convert these into a risk register with mitigation actions, governance, and monitoring KPIs.
Outcome: risk-aware plan that stakeholders (operations, compliance, finance) can support.
5) Scalability pathways and partner ecosystem design
Circular models scale through ecosystems—not solo effort. We define:
Partner roles and incentives (who gets paid for what, when)
Quality standards and acceptance criteria
Commercial structure options (revenue share, service fees, performance metrics)
Phased scaling plan (pilot → controlled rollout → multi-site replication)
Outcome: a practical, scalable pathway with “next steps” you can execute.
What we offer (service components)
Circular Economy Strategy Development
We create a clear circular strategy aligned with business goals—cost, resilience, compliance, and growth. This includes opportunity mapping, prioritisation, and measurable targets.
Resource Optimization & Waste Reduction
We identify where resource losses occur and define engineering + operational improvements to reduce waste and improve efficiency—often delivering quick wins while building the longer-term circular loop.
Product Lifecycle Extension Programs
We design programs that keep products in use longer through:
repairability and upgrade pathways
refurbishment/remanufacturing operations
warranties and quality grading systems
reverse logistics design and customer incentives
Sustainable Business Model Design
We design revenue models that make circularity profitable:
subscription/service models
buy-back and resale channels
performance contracting
secondary market and channel strategy
Circular Supply Chain Integration
We integrate circular flows into procurement, suppliers, logistics, and operations—ensuring traceability, compliance, and quality standards.
Key benefits (what you gain)
Reduced operational costs through resource efficiency
Circular loops reduce dependency on volatile inputs and lower the cost of waste handling, disposal, and inefficiencies.
New revenue streams from waste-to-value
Recovered materials, refurbished products, and second-life components can create high-margin offerings when quality and go-to-market are designed correctly.
Enhanced brand reputation and market positioning
Buyers and partners increasingly prefer suppliers with credible, measurable sustainability performance—especially where reporting requirements are tightening.
Compliance with environmental regulations
We design circular programs that are compliance-aware from the start, reducing regulatory and audit risk while improving reporting readiness.
Where circular innovation creates the biggest impact
Battery reuse and second-life value chains
Second-life batteries can unlock value through:
grading, safety screening, and state-of-health (SoH) assessment
repurposing into stationary energy storage or low-demand applications
designing warranty and liability structures that don’t destroy margin
standardised testing + data traceability for buyer confidence
Industrial symbiosis for manufacturing and infrastructure
Industrial symbiosis is often the fastest route to “waste-to-value” at scale—when the economics are right and partner incentives are aligned. We help identify practical matches and structure them into implementable flows.
Circular product and packaging systems
For product-based businesses, circularity often starts with redesign:
modular components
repairability and parts availability
take-back and refurbishment operations
packaging loops and reverse logistics
Circular procurement and supply chains
Circular supply chains require:
supplier standards and traceability
reverse logistics, sorting, and quality grading
data and documentation to support compliance and customer requirements
Deliverables you can expect
Depending on scope, your project typically includes:
Circular opportunity map (ranked by value, feasibility, time-to-impact)
Business model blueprint (operating model, stakeholders, incentives, flows)
Techno-economic validation model (assumptions, scenarios, sensitivity analysis)
Risk register + mitigation plan (compliance, liability, quality, operational risks)
Implementation roadmap (pilot plan, timeline, governance, KPIs)
Scalability pathway (partner strategy, replication plan, data and QA standards)
These deliverables are built to be used—not just presented.
Our process (what working with us looks like)
Phase 1 — Discovery & Data (1–3 weeks)
Quick alignment, data gathering, and current-state mapping.
Phase 2 — Model Design (2–4 weeks)
Develop candidate circular business models and shortlist best options.
Phase 3 — Validation & Risk (2–4 weeks)
Run TEA, build risk register, refine the implementation design.
Phase 4 — Blueprint & Scale Plan (1–3 weeks)
Create the actionable roadmap and scale strategy.
Timelines depend on data availability, stakeholder access, and whether you’re targeting a pilot site or a full multi-site transformation.
What makes Greenovation Solutions different
Many circular economy projects fail because they overfocus on sustainability narratives and underfocus on the mechanisms that make circularity work: quality, economics, risk, and scaling.
We bridge the gap between:
regulation (what you must do),
engineering reality (what’s possible and safe),
and commercial strategy (what can actually make money).
That’s how circularity becomes a business advantage, not a cost centre.
Ready to build a circular business model that scales?
If you’re looking at circular innovation for battery reuse, resource optimisation, product lifecycle extension, or industrial symbiosis, we can help you move from concept to implementation—fast, and with the numbers to support decisions.
Next step: Share a short overview of your product/process, waste streams (or end-of-life assets), and your target outcome (cost reduction, compliance, new revenue, or all three). We’ll respond with a recommended starting scope and what data we need to validate feasibility.
FAQ: Circular Business Model Innovation
What is a circular business model, in simple terms?
A circular business model is designed so products and materials stay in use longer—through reuse, repair, refurbishment, remanufacturing, or recycling—while still generating profit and meeting compliance requirements.
Do you only work on battery-related projects?
No. Batteries are a major focus due to fast-growing end-of-life volumes and regulatory pressure, but we also support manufacturing, logistics, infrastructure, and product-based industries where circularity improves cost and resilience.
What data do you need to start?
Typically: baseline cost structure, material/product flow information, waste handling costs, current suppliers/logistics, and any compliance constraints. If data is limited, we can start with structured assumptions and validate progressively.
How do you prove the model is financially viable?
We build a techno-economic validation (TEA) model with scenario and sensitivity analysis—showing what drives unit economics, where break-even sits, and what operational thresholds must be achieved.
Can you help beyond strategy—into implementation?
Yes. Our focus is implementation blueprints and scale pathways. If you need partner mapping, pilot design, KPI tracking, and governance setup, we include that in scope.
SEO suggestions (optional to add to the page)
Meta Title (≤ 60 chars):
Circular Business Model Innovation | Greenovation Solutions
Meta Description (≤ 160 chars):
Build circular economy business models that reduce costs, unlock new revenue, and meet regulations—with techno-economic validation and scale-ready blueprints.
Primary keywords to target:
circular business model innovation, circular economy consulting, circular economy strategy, product lifecycle extension, circular supply chain, industrial symbiosis, battery reuse business model, waste to value, techno-economic analysis circular economy
Suggested internal link anchors:
Battery reuse & second-life strategy
Techno-economic validation (TEA)
Circular supply chain integration
Risk profiling and compliance readiness
If you want, I can also tailor this article to a specific target market (UK/EU vs global), add an industry-specific mini case study (e.g., EV batteries, manufacturing waste streams, or logistics packaging loops), and adapt the tone to match the style of the rest of your website.